Windows Security, previously known as Windows Defender, is a Windows-native antivirus and protection software that prevents your PC from malicious infection, ransomware attacks, and other online threats. To keep up with the ever-growing threats and attacks, Windows Security needs to be updated regularly with security patches and signature updates.
However, once you have configured a wired or wireless network (whichever your device is connected to as a metered connection), it will restrict Windows Security from receiving signature updates through Windows Update. This will mean your device will no longer be able to protect itself from newer, zero-day threats.
Table of Contents
A metered connection is often used to restrict background internet usage so that the tasks being performed in the foreground get greater bandwidth. With this benefit, the caveat, which we have already mentioned, is that Windows Security is no longer able to update.
That said, there are still several ways to get Windows Security to update while connected to a metered connection. This way, you won’t have to disable the metered connection to keep your system secure from the latest threats.
How to Enable Windows Security Signature Updates Over Metered Connection
There are several methods to allow Windows Security to keep updating normally through Windows Update even though you are connected to a metered connection.
Using Windows PowerShell
PowerShell is a powerful command-line tool used to perform administrative tasks. Follow these steps to allow Windows Security to update regularly over a metered connection:
-
Paste the following cmdlet to enable Windows Security to update over a metered connection:
Set-MpPreference -MeteredConnectionUpdates 1
Enable Windows Security to update using PowerShell
After running this command, Windows Security will now automatically update, even if your PC is connected to a metered internet connection.
If you wish to disable Windows Security from updating in the future, use the following cmdlet:
Set-MpPreference -MeteredConnectionUpdates 0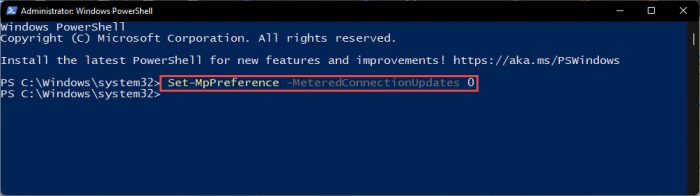
From Group Policy
Another way to allow Windows Security to continue to update over a metered connection is by using the Group Policy Editor. Here is how to do it:
-
Open the Group Policy Editor by typing in gpedit.msc in the Run Command box.
Open Group Policy Editor -
Now navigate to the following location from the left pane:
Computer Configuration >> Administrative Templates >> Windows Components >> Microsoft Defender Antivirus >> Security Intelligence Updates
-
Here, double-click on the policy “Allow Microsoft Defender Antivirus to update and communicate over a metered connection.”

Open Group Policy -
Select the Enabled radio button from the policy, then click Apply and Ok.

Enable the policy -
To implement the changes, run the following cmdlet in an elevated Command Prompt:
GPUpdate /Force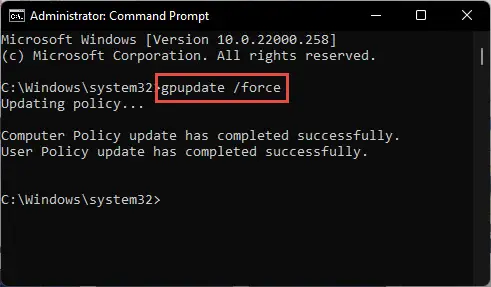
gpupdate force latest
That’s it! Windows Security will now update normally even on a metered connection.
If you want to revert to these changes, return to the same policy as in step 3 above, and select the Not Configured or Disabled radio button.
From Task Scheduler
You can program your operating system to continue checking for Windows Security updates by creating scheduled tasks. Here is how:
-
Open up the Task Scheduler by typing in taskschd.msc in the Run Command box.

Open Task Scheduler -
From the left pane, right-click “Task Scheduler Library” and then click Create basic task from the context menu.

Create new task -
From the Create basic task wizard, enter a name for the task and click Next.

Name the task -
On the next screen, choose a time interval for the task to run, then click Next.

Choose interval to check for update -
Now provide details for the schedule of the task and click Next.

Provide relevant details for scheduling -
Select “Start a program” and click Next.

Select action to perform -
On the next screen, paste the following details into the respective text fields, and then click Next.
Under “Program/script”:
"C:\Program files\Windows defender\MpCmdRun.exe"
In front of “Add arguments (optional)”:
-SignatureUpdate

Provide program details -
Now click Finish to complete the task creation.

Complete task creation
The task will now run at selected intervals to check for Windows Security signature updates, even if the device is on a metered connection.
If you want to stop running this task and check for updates, simply delete the task.

From Windows Registry
You can also achieve the same task using the Windows Registry Editor. However, we suggest that you only adopt this method if you are having issues with other methods.
Note: Misconfiguration of critical values in the system’s registry could be fatal for your operating system. Therefore, we insist that you create a system restore point before proceeding forward with the process.
-
Open the Registry Editor by typing in regedit in the Run Command box.
Open the Registry Editor -
Now paste the following into the address bar at the top for quick navigation.
Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows Defender

Navigate to Windows Defender Key quicker -
Right-click the “Windows Defender” Key, expand New, then click Key from the context menu.

Create new key Name this new Key “Signature Updates.”
-
Now right-click the “Signature Updates” Key, expand New, then click DWORD (32-bit) Value from the context menu.

Create new DWORD Name this DWORD “MeteredConnectionUpdates.”
-
Double-click MeteredConnectionUpdates and set its Value Data to 1. Then click Ok.

Set Value Data -
Now restart your computer for the changes to take effect.
Once it reboots, Windows Security will now update automatically through Windows Update, even if your PC is connected to a metered connection.
If you want to disable Windows Security from updating over metered connections, simply delete the Value MeteredConnectionUpdates, or set its Value Data to 0.

If you find that these methods are lengthy, download the registry files given below and run them to enable or disable Windows Security from updating over a metered connection.
 Allow Windows Security to Update over Metered Connection.zip (426 bytes, 446 hits)
Allow Windows Security to Update over Metered Connection.zip (426 bytes, 446 hits)
 Block Windows Security to Update over Metered Connection.zip (427 bytes, 398 hits)
Block Windows Security to Update over Metered Connection.zip (427 bytes, 398 hits)
Of course, a system restart would be required to finalize the changes made from these registry files.
Final Thoughts
Windows Security is one of the most critical components of the Windows operating system. If it were to be outdated, then it would rather not exist at all. Security threats are growing exponentially every second. Thus, we must not let our guard down with security software that does not have the latest signature updates.
Therefore, we suggest that you allow Windows Security to always be able to update itself if you are mostly connected to a metered connection.





